Ozone is a strong oxidant, a light blue gas with a fishy smell, it is heavier than air, and at a certain temperature, it will decompose itself into oxygen over time. when the human body inhales ozone, it will irritate and damage the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract. The degree of damage depends on the concentration of ozone inhaled and the length of inhalation.Ozone always exists in the environment we live in, the general concentration is around 0.015PPM, and we can't feel its existence. When the concentration reaches 0.02PPM, sensitive people will smell ozone.
The US UL867 safety standard for ozone is ≤0.05PPM, and the EU standard is formulated with reference to the US standard. my country's standard GB simply says that UL867 means that under laboratory conditions (temperature 25°C, humidity 50%), the cumulative concentration produced by any ozone source cannot exceed 0.05PPM.The direct damage of ozone to the human body will cause significant damage to the human respiratory system, cause eye irritation, cause respiratory diseases, and even asthma.
At the same time, it has a certain hidden harm to the human body. If you are in an environment where ozone exceeds the standard for a long time, your heartbeat will speed up and you will be restless. The medical community has reached a consensus that ozone can induce some latent or invisible diseases in the human body.
OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) *OSHA Permissible Exposure Limit (PEL) guidelines for O3 in the workplace are based on time-weighted averages (TWA). 0.1 ppm for 8 hour work shift for a 40 hour work week.*
-OSHA requires that if you are generating ozone that you measure this ozone level for safety purposes
-The OSHA website cites the following exposure limits for ozone in the workplace:
*0.1 ppm PEL for 8 hours per day (TWA) exposure for General Industry
*0.1 ppm PEL for 8 hours per day (TWA) exposure for Construction Industry
*0.1 ppm PEL for 8 hours per day (TWA) exposure for Shipyard Employment
*0.3 ppm Short Term Exposure Limit (STEL) for a 15 minute time weighted average (TWA) exposure which is not to be exceeded at any time during a workday even if the time-weighted average is below the PEL.
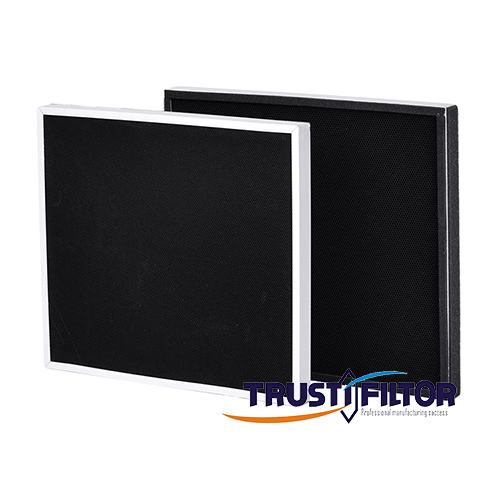


 The role of ozone removal filter in air purifier
The role of ozone removal filter in air purifier
 What are the industrial applications of oil fume removal filters
What are the industrial applications of oil fume removal filters
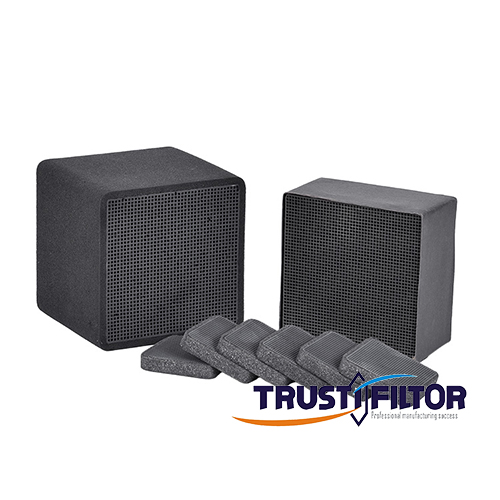 Industrial applications of ozone removal filters
Industrial applications of ozone removal filters
 The difference between baffle grease filter and mesh grease filter
The difference between baffle grease filter and mesh grease filter